Dave Ulrich is the Rensis Likert Professor Emeritus at the University of Michigan and a partner at the RBL Group. He has published over 200 articles and book chapters and 30 books.
He edited Human Resource Management for ten years, served on editorial board of four other journals and on the Board of Directors for Herman Miller (16 years), has spoken to large audiences in 90 countries; performed workshops for over half of the Fortune 200, received numerous lifetime achievement awards, and is a Distinguished Fellow in the National Academy of Human Resources.
He posts weekly and comments daily on LinkedIn. His work creates ideas with impact about how to deliver stakeholder value through human capability (talent + organization + leadership + HR).
Q1- How has the changing role of HR reshaped talent acquisition strategies in today’s dynamic business environment?
HR is less about “HR” work and more about creating value for all stakeholders. Talent is a primary element of HR work and means that people (sometimes labelled workforce, employees, people) have the right competencies (knowledge, skills, and aptitude) to accomplish tasks that deliver value to all stakeholders. The “human” in human resource has broadened.
Stakeholders are all the “human” beings who engage with the organization, including employees and also customers, investors, communities. Talent represents the core ingredients of any organization who add value to all these human stakeholders.
Today, acquiring talent implies being the employer of choice of employees customers would choose, using both human and technology (agentic AI) together, and managing a hybrid workforce, all designed to deliver stakeholder value.
Q2- With increasing digitalization, how can HR maintain a human touch during recruitment and onboarding?
A simple and emerging formula for successful talent is: AI (artificial intelligence) * AI (authentic intimacy). The “*” means that one without the other will not work. Artificial intelligence comes through both agenticAI which means systems that deliver efficiency through bots that streamline recruiting and on boarding and genAI which provides information for getting the right talent hired and on board.
The human touch comes when employees feel that are known and cared for, when standard policies are personalized to the employee situation, and when employees do the innovative and creative work of shaping the future.
Q3- What new skills must TA professionals develop to stay relevant in the evolving talent landscape?
A number of groups have studied HR Competencies for TA and other HR professionals. Drawing on the research and practice by these exceptional groups, along with other studies of HR competence, both expected and emerging competencies needed for HR professionals can be organized into six timeless domains.
Expected competencies are foundational and fundamental to effective HR. Emerging competencies are those that groups have identified that are needed to respond to changing work conditions today.
Figure: Expected and Emerging Competencies for HR Professionals
| HR Skill Domain | Expected and Emerging Competencies |
| Accelerate Business | Know business context and environmental trendsDesign and deliver strategyDeliver value to all stakeholders (customers, investors) |
| Advance Human Capability | Align, design, and deliver latest HR practices for talent, organization, and leadershipOffer integrated human capability solutions |
| Make Change Happen | Drive agility and change throughout the organization Get things done to respond to chaos and disruption |
| Use GenAI and Analytics for Information | Recognize latest agentic and genAI trends for improving HR services and provide guidance by understanding and meeting stakeholder needsUse analytics to improve decision making and prioritization |
| Create Organization Culture | Design and deliver the “right” culture that creates value focused on firm brand outside made real insideBecome the architect of making culture happen |
| Demonstrate Personal Proficiency | Be clear about personal purpose Build credibility (trust) with all stakeholders Demonstrate and model the values of the organization Think critically about the future Have courage to influence others |
Q4- How can onboarding be designed to reflect evolving employee expectations around purpose, flexibility, and inclusion?
When a new employee enters an organization, they want to make sure they know how they contribute to the organization’s marketplace success. Best companies focus on boarding not just with someone’s job or role, but with customers: who they are, why they purchase product or service, and how to anticipate and meet their needs.
When new employees better understand the organization’s customer value proposition, they can see how their daily work delivers this value.
An employee’s purpose fulfils a customer’s expectation; organization flexibility adapts to customer requirements; and inclusion means making the customer part of the decision and on boarding process.
Teaching employees customer expectations has come when new employees act as and become customers, examine market research, and personally engage with customers.
One convenience store had new employees go to the stores to interview customers about why they were shopping in their store. This was less about market research ad more about new employees having a customer first mindset.
With a customer mindset, the other on board activities have a clear focus: logistics (computer, work space), team (assimilation onto a team with peers), leadership (having a mentor who coaches), and first assignments (early successes).
These traditional on boarding experiences through the agenda of customer value ensure that a new employee feels like a value creator for others.
Q5- What role does Emerging Technology play in shaping future-ready hiring and onboarding experiences?
AI is THE rage! It is on top of every trends list, discussed at nearly every conference and podcast, and recommended by all the leading consulting firms.
AI has been advocated as something that will transform the global economy, reduce human error, increase GDP by 7 percent, improve the study of proteins and scientific discovery, upgrade patient care, change the nature of the workforce, reinvent industries (education, entertainment, health care, retail, cybersecurity, manufacturing), and even predict the weather more accurately.
Estimates are that 82 percent of global firms are using or exploring AI, and the number of research papers on AI are doubling every 24 months.
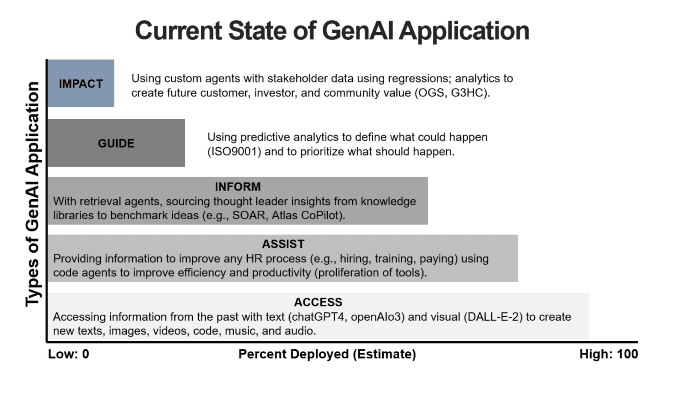
Most talent decisions rely on information: How to set criteria, source, screen, secure, and on board talent? I suggest five waves of how HR information can be used to better manage talent (figure 2b).
Each of these five uses of genAI for talent have different estimated deployment rates and innovations that are rapidly evolving (see figure 3).
Figure 2: Evolution of GenAI for Talent

Figure 3: Deployment and Innovations in GenAI for Talent Information
As these technology-enabled talent tools are deployed, organizations will acquire, deploy, motivate, engage, and retain the talent who will deliver stakeholder value.
Thank you, Dave Ulrich!
Note: We are also on WhatsApp, LinkedIn, and YouTube, to get the latest news updates. Subscribe to our Channels. WhatsApp– Click Here, YouTube – Click Here, and LinkedIn– Click Here.



